Table of Links
-
Background and 2.1. Related Work
2.2. The Impact of XP Practices on Software Productivity and Quality
3.2. Team Velocity Model
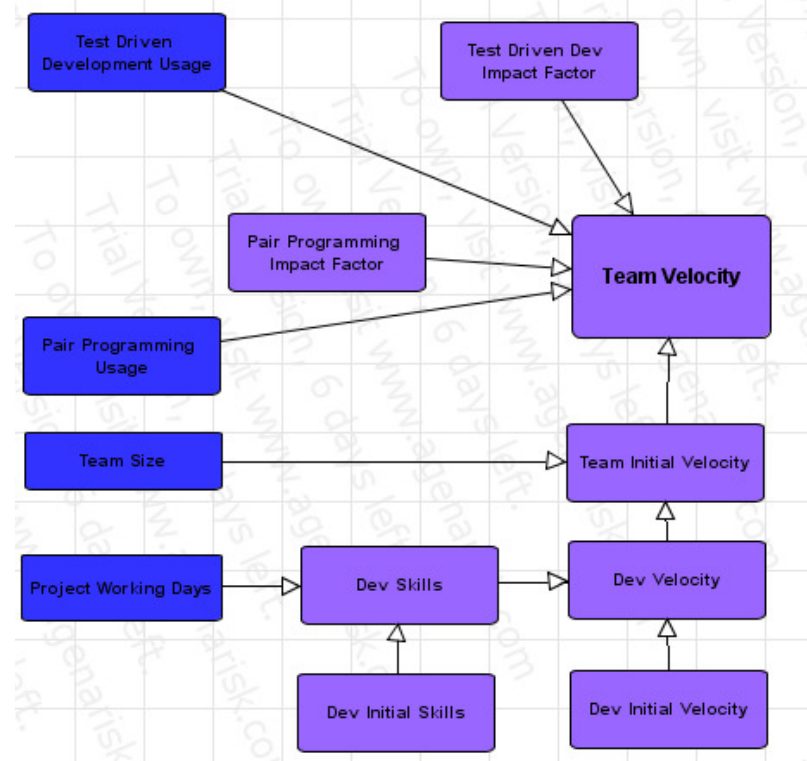
Team velocity, measured in number of user stories per day, is a good representation for the productivity of the team. The model is shown in Figure 4. Three main factors affect the team velocity in XP, namely: Team XP skills, Pair Programming usage and Test Driven Development usage.
The main components of the model are:
-
Developer initial skills: random number uniformly distributed over the range [1,10] [4]. This number represents the developer ability to develop software.
-
Developer skills: Dev. Skills depend on two main factor, namely: dev_initial_Skills and project_working_days. This value represents increasing developer skills with time. It can be calculated as described in Equation (1)[4], where LC is the learning coefficient, typically 0.009 [4].
Dev_skills = log(dev_initial_Skills + project_working_days*LC) Equation (1)
-
Developer Initial Velocity: represents the number of story points the user can develop per day. According to empirical data [4], a random variable following the normal distribution with mean 4 and standard deviation 1 was considered to represent this value.
-
Dev. Velocity: this value represents the impact of the developer skills on his velocity. It is calculated as the summation of the Dev. Initial Velocity and the dev. Skills factor.
-
Team Initial Velocity: represents the number of story points the team can develop per day. It can be calculated as the product of Team Size times Dev. Velocity.
-
Pair Programming Impact Factor (pp_Impactfactor): This factor represents the impact of adopting Pair Programming practices in the team velocity. This value was set to a normal distribution random variable with mean 23 and standard deviation 20. This value was set according to a number of studies. Those studies show that Pair Programming reduces the Project time by a factor starting from 0 (no change) in some cases to 45% in others. More data regarding those studies is available in the Background section.
-
Test Driven development Impact Factor (TDD_Impactfactor): This factor represents the impact of adopting Test Driven Development practices in the team velocity. This value was set to a normal distribution random variable with mean -32 and standard deviation 42. This value was calculated according to number of studies [4]. Those studies show that Test Driven Development results in increasing the project time by a factor starting from 0 (no increase) in some studies to 80% in others. A review of those studies is available in the Background section.
-
Team Velocity: This value represents the number of story points the team can develop per day taking into account all the previous factors. Equation 2 represents this value.
Team Velocity = Team_initial_velocity* (1+PP_usage*PP_ImpactFactor/100)*
(1+TDD_usage*TDD_impactfactor/100) Equation (2)
Authors:
(1) Mohamed Abouelelam, Software System Engineering, University of Regina, Regina, Canada;
(2) Luigi Benedicenti, Software System Engineering, University of Regina, Regina, Canada.
This paper is

